KIRCHOFF'S LAW

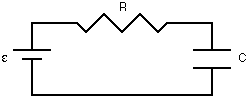
1. Definition Kirchhoff's laws quantify how current flows through a circuit and how voltage varies around a loop in a circuit. Kirchhoff's 1st law states that current flowing into a node (or a junction) must be equal to current flowing out of it. This is a consequence of charge conservation. Kirchhoff's 2nd law states that the sum of all voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must equal zero. This is a consequence of charge conservation and also conservation of energy. 2. Formula Where: I stands for the electric current (A) Where: V stands for voltage (Volt) I stands for electric current (A) 3. Important Figure Gustav Kirchhoff was a famous German physicist born in 1824. Gustav Kirchhoff studied mathematical physics at Albertus University of Konigsberg, graduating in 1847. In 1845, Kirchhoff extended Ohm's work by developing a method to understand and predict the behavior of much more complex circuits. ...